Verified news sources are crucial in today’s information-saturated world. This guide delves into the essential aspects of identifying and evaluating reliable news, providing insights into various verification methods and common biases.
Understanding the methods news organizations use to verify information, from fact-checking to source verification, is vital for discerning truth from falsehood. This exploration will equip readers with the tools necessary to critically assess news content and avoid misinformation.
Defining Verified News Sources
A verified news source is a crucial component of a well-informed citizenry. It provides reliable and accurate information about events and issues, enabling individuals to make informed decisions. Distinguishing between verified and unreliable sources is essential in navigating the complexities of modern media.Verifying news sources is more than just relying on a name; it involves a multifaceted approach to assessing credibility.
It encompasses meticulous fact-checking, transparent reporting practices, and a commitment to ethical journalism. This process is critical in combating misinformation and ensuring the public receives accurate and unbiased information.
Characteristics of a Verified News Source
A verified news source exhibits several key characteristics. These include a commitment to journalistic ethics, a track record of accuracy, and an absence of significant bias. Transparency in sourcing and methodology further cements the reliability of the information.
Methods for Verifying News Sources
Several methods are employed to verify the accuracy and reliability of news sources. Independent fact-checking organizations play a critical role in scrutinizing claims and reports. These organizations utilize diverse methods, including cross-referencing information from multiple sources and examining the credibility of the cited evidence. Furthermore, reputable news organizations have established internal fact-checking teams that rigorously evaluate information before publication.
Comparison of News Organization Types
| News Organization Type | Verification Processes | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reputable Newspapers (e.g., The New York Times, The Guardian) | Employ multiple reporters, editors, and fact-checkers; extensive research and corroboration; emphasis on source verification. | Well-established reputation, deep journalistic tradition, thorough fact-checking, diverse perspectives. | Potentially slower dissemination of information; may be influenced by editorial slant, though often mitigated by checks and balances. |
| News Agencies (e.g., Reuters, Associated Press) | Utilize a global network of correspondents; strict adherence to journalistic standards; rigorous editing and verification procedures. | Extensive global reach, neutral reporting style (ideally), high standards for accuracy. | Potentially susceptible to bias if not consistently monitored and verified; rely on consistent reporting practices, which may sometimes lag behind breaking news. |
| Online Publications (e.g., BBC News, NPR) | Vary in verification processes; some have strong journalistic traditions, others may lack rigorous fact-checking; reliance on established journalistic principles. | Wide reach and accessibility; often incorporate diverse perspectives. | Varying levels of credibility; may lack the resources or experience of established news organizations; susceptibility to misleading headlines or clickbait tactics. |
The table above provides a comparative overview of verification processes within different news organizations. Each type has strengths and weaknesses, highlighting the importance of critical thinking and awareness when evaluating any news source.
Recognizing Unreliable Sources
Unreliable news sources often exhibit patterns of inaccuracy, bias, and lack of transparency. These sources frequently rely on unsubstantiated claims, lack of credible sourcing, and/or present biased information to sway opinions.
Identifying Verification Methods
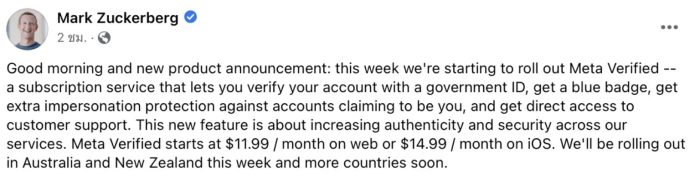
Verifying news content is a crucial process in ensuring its accuracy and reliability. News consumers must be discerning and aware of the methods employed to assess the validity of information presented. This section details various verification strategies used by reputable news organizations, emphasizing the importance of fact-checking and investigative journalism.Verification methods are multifaceted and rely on a combination of techniques to validate information.
These techniques range from rigorous source checks to in-depth investigations, ensuring that news presented to the public is credible and trustworthy.
Fact-Checking Procedures
Fact-checking procedures are essential in verifying the accuracy of news claims. They involve a systematic examination of information to determine its truthfulness and validity. This process typically includes cross-referencing data with multiple independent sources, consulting expert opinions, and scrutinizing the context of statements. A comprehensive fact-check considers the potential biases or motivations of the source. The importance of fact-checking lies in its ability to prevent the spread of misinformation and maintain public trust in the news media.
Investigative Journalism Practices
Investigative journalism plays a significant role in verifying news claims. Investigative journalists employ a variety of techniques, such as conducting extensive research, interviewing sources, and analyzing documents to uncover hidden truths and expose potential biases or inaccuracies. They often delve into complex issues, meticulously verifying claims through painstaking research and verification of sources. This form of journalism holds power to uncover wrongdoing and shed light on important issues, serving as a critical check on the accuracy of information disseminated.
Examples of Investigative Journalism Practices
- Investigative journalists meticulously review documents, often obtained through legal means or public records requests, to corroborate or refute claims. This includes scrutinizing financial records, government reports, or internal communications. Examples include investigations into political corruption or corporate wrongdoing, where journalists use publicly available data to uncover patterns and inconsistencies.
- Interviews with multiple sources are a cornerstone of investigative journalism. These interviews, conducted with care and skepticism, help to corroborate or challenge initial claims. For instance, journalists might interview witnesses, experts, and those directly involved in an event to build a comprehensive picture and identify potential biases or conflicting accounts.
- Analysis of data and statistical information is crucial in investigative journalism. Journalists use data to expose trends, patterns, or anomalies that might indicate inaccuracies or hidden agendas. For example, in reporting on the impact of a new policy, journalists might analyze statistical data from various sources to assess its effectiveness and impact on different segments of the population.
Role of Independent Fact-Checking Organizations
Independent fact-checking organizations play a critical role in verifying news. These organizations, free from the influence of any particular news outlet, provide an objective assessment of claims made in news reports. They utilize various fact-checking methodologies to verify information, including the examination of sources, context, and potential biases. The existence of these independent organizations helps maintain journalistic integrity and ensures accountability.
Source Verification
News organizations employ various techniques to verify sources. This includes checking the credentials and reputation of individuals providing information, corroborating their statements with other sources, and assessing potential conflicts of interest. Source verification ensures that information presented is accurate and trustworthy. It also helps identify possible biases or motivations that might influence a source’s statements.
Evaluating Credibility
Assessing the credibility of a news source is a crucial step in discerning reliable information. A critical approach to evaluating news sources ensures that the information consumed is accurate, unbiased, and trustworthy. This process involves examining various factors beyond simple verification, including the source’s history, author expertise, and potential biases.Evaluating a news source’s credibility goes beyond just checking if it’s a verified source.
It requires a deeper dive into the source’s methods and motivations, understanding that even reputable sources can sometimes fall short of ideal standards. This comprehensive evaluation is essential for responsible information consumption in today’s complex media landscape.
Indicators of a Credible News Source
Identifying credible news sources relies on recognizing certain characteristics. These characteristics signal a commitment to accuracy, objectivity, and responsible reporting. A credible news organization generally demonstrates transparency in its editorial process, providing clear guidelines on how it verifies information and presents its content.
- Accuracy: A reliable source meticulously checks facts and avoids errors in reporting. For instance, a news organization should thoroughly verify claims before publishing, and should promptly correct any factual inaccuracies. This demonstrated commitment to accuracy fosters trust and reliability.
- Objectivity: Credible news sources strive to present information neutrally, avoiding bias and presenting multiple perspectives on a given issue. The source should not favor one side of an argument over another.
- Independence: News organizations that operate independently from political or commercial interests are more likely to provide unbiased reporting. Transparency in funding sources is often a key indicator of independence.
- Reputable Journalism Practices: Credibility is built on a foundation of journalistic principles. Sources should adhere to ethical standards and avoid sensationalism or misleading information.
- Transparency: Transparency in reporting processes builds trust and allows readers to understand how information is gathered and presented. A source that clearly explains its verification methods and editorial standards enhances credibility.
Author Expertise and Reputation
Author expertise and reputation significantly influence a news source’s credibility. A piece written by a subject matter expert, or one with a proven track record of accuracy, significantly enhances the credibility of the information presented. The author’s potential conflicts of interest also need consideration.
- Expertise: An author with expertise in a specific field can provide a more nuanced and reliable perspective. Identifying the author’s credentials, such as educational background or professional experience, is important in determining their expertise.
- Reputation: A well-respected author with a history of accurate reporting tends to lend credibility to their work. Past publications and their reception by the community can be a factor in assessing the author’s reputation.
Assessing Objectivity and Neutrality
Evaluating objectivity and neutrality is a critical component of assessing credibility. A neutral source presents different perspectives on a topic, avoids emotional language, and does not favor one side over another. Objectivity in a news article is shown through a balance of viewpoints.
- Balanced Perspective: A credible news source will present multiple viewpoints on a given issue, acknowledging different perspectives and providing evidence to support each side of the argument.
- Lack of Emotional Language: Credible sources typically avoid inflammatory language or emotional appeals to manipulate the audience’s opinion. Facts and data should be the core of the reporting.
- Avoiding Bias: A truly objective source avoids promoting specific agendas or ideologies. Any perceived bias should be transparently disclosed, adding to the source’s trustworthiness.
Identifying Potential Biases
Recognizing potential biases in a news source is a vital aspect of evaluating credibility. Bias can manifest in subtle ways, including the selection of sources quoted, the framing of the narrative, and the choice of specific details emphasized.
- Source Selection: A source that predominantly quotes experts from one side of an issue may signal a bias. Assessing the variety of sources quoted can help identify potential biases.
- Narrative Framing: The way a story is presented can also indicate potential bias. The selection of specific details or the emphasis placed on certain aspects of the story can sway the audience’s interpretation.
- Language and Tone: The language and tone used in the article can also signal potential bias. The use of inflammatory language or emotional appeals can indicate a deliberate attempt to influence the reader’s opinion.
Analyzing Bias in Reporting
News reporting, while striving for objectivity, can be susceptible to various forms of bias. Understanding these biases is crucial for discerning accurate and reliable information. Recognizing and mitigating the impact of bias on news consumption empowers individuals to form informed opinions and make sound judgments.Bias in news reporting can significantly affect the accuracy and reliability of information presented.
Readers who are unaware of these biases might be misled into accepting one-sided perspectives as factual accounts. Understanding the different types of bias, how they manifest, and their potential impact is essential for critical consumption of news.
Types of Bias in News Reporting
Different forms of bias can influence the presentation of news. Recognizing these biases is vital for discerning potentially slanted information.
- Political Bias: News outlets might favor certain political viewpoints or parties over others. This could involve selecting news stories that align with a specific political ideology or framing events in a way that supports a particular political stance. For instance, a news source might repeatedly feature criticism of one political party while neglecting or downplaying criticism of another.
- Confirmation Bias: News outlets might tend to select and highlight information that confirms existing beliefs or perspectives. This might manifest as presenting stories that reinforce pre-conceived notions, potentially ignoring contradictory evidence. An example would be a news source that consistently focuses on the negative impacts of a particular policy without exploring potential positive effects.
- Ideological Bias: News outlets might favor a specific ideology, such as conservative or liberal viewpoints. This might influence the selection of stories, their framing, or the language used to describe events. For example, a news source might consistently use negative language when discussing government actions, suggesting a predisposition against certain policies or institutions.
- Cultural Bias: A news source might subtly favor or present a certain culture over others, potentially marginalizing or misrepresenting underrepresented groups. For instance, a news outlet might primarily feature stories from or about one culture, leading to a skewed perception of global events or issues.
- Economic Bias: News outlets might favor certain economic viewpoints or interests. This might involve emphasizing the perspectives of particular businesses or industries while neglecting the concerns of others. An example of this would be a news source that consistently promotes the interests of large corporations without considering the effects on smaller businesses or consumers.
Impact of Bias on News Consumption
Bias in news reporting can distort the perception of reality. Understanding its effects on news consumption allows for critical evaluation.
- Misleading Conclusions: Readers might draw incorrect conclusions or develop biased perspectives due to selective reporting or presentation of information.
- Reinforcement of Stereotypes: Bias can reinforce existing stereotypes or prejudices, potentially creating a skewed understanding of different groups or cultures.
- Distorted Understanding of Events: Biased reporting can lead to an incomplete or inaccurate understanding of complex events, potentially hindering informed decision-making.
Strategies to Mitigate Bias
Critical evaluation of news sources is essential for minimizing the impact of bias on news consumption. Developing strategies to mitigate bias is key to ensuring informed decision-making.
- Seek Multiple Perspectives: Reading news from diverse sources can help balance potential biases. Comparing accounts from different news outlets can offer a more comprehensive understanding of events.
- Examine the Source’s Reputation: Consider the track record and reputation of the news outlet. Reliable news organizations generally adhere to journalistic standards and practices.
- Analyze the Language Used: Pay close attention to the language used in the reporting. Neutral language tends to suggest objectivity, whereas loaded language might indicate bias.
- Consider the Source’s Potential Conflicts of Interest: Investigate potential conflicts of interest, such as financial ties or affiliations, which might influence the reporting.
Common Biases and Their Impact
Understanding common biases helps evaluate news sources critically.
| Bias Type | Potential Impact on Readers |
|---|---|
| Political Bias | Readers might develop skewed views on political issues, favoring one side over another. |
| Confirmation Bias | Readers might be less open to contradictory information, reinforcing existing beliefs. |
| Ideological Bias | Readers might be exposed to a narrow range of perspectives, limiting their understanding of different viewpoints. |
| Cultural Bias | Readers might develop misconceptions or stereotypes about different cultures. |
| Economic Bias | Readers might not receive a balanced view of economic issues, potentially overlooking the concerns of various stakeholders. |
Understanding News Dissemination
News dissemination is a complex process, involving multiple stages and platforms. From initial reporting to final consumption, understanding the pathways of information is crucial for discerning credible news from misinformation. This section explores the various methods of news distribution, highlighting the role of different platforms and the potential for misinformation in each.
News Dissemination Across Platforms, Verified news sources
News is disseminated through a multitude of channels, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Traditional print media, such as newspapers and magazines, still hold significant influence, though their reach is often geographically limited. Digital platforms, including websites, blogs, and social media, have dramatically expanded the accessibility of news.
Examples of Different Platforms and Verification Processes
Reputable news organizations typically have robust verification processes, including fact-checking teams and rigorous journalistic standards. For example, the Associated Press (AP) employs a large team of editors and reporters to verify information before publication. Online news outlets often rely on similar procedures, though their resources and staffing may vary. Social media platforms, while offering immediate dissemination, are often susceptible to the rapid spread of misinformation.
These platforms often rely on user reporting and algorithmic detection to flag potentially false content, but these systems are not always effective. Some platforms, like Twitter, have implemented verification programs to help distinguish legitimate news accounts from others.
Social Media’s Role in Disseminating Verified News
Social media platforms, while often associated with the rapid spread of misinformation, can also be effective tools for disseminating verified news. Reputable news organizations utilize social media to share breaking news, analysis, and other content. The speed of dissemination on these platforms can be invaluable for immediate reporting, but it also necessitates careful verification by users. News organizations often partner with influencers or prominent figures on social media to amplify verified news to broader audiences.
News Sharing and Consumption Across Channels
News consumers often engage with information across multiple channels. A reader might begin by reading an article on a news website, then share a relevant quote or excerpt on social media. This interconnectedness of channels amplifies the reach of verified news but also increases the potential for misinformation to spread. The process is not always linear, and the order of consumption can vary depending on individual preferences and habits.
Comparison of News Distribution Channels and Misinformation Potential
| Distribution Channel | Verification Process | Misinformation Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Print Media | Generally rigorous, with established fact-checking procedures. | Lower, but not nonexistent. Can still suffer from bias or errors. |
| Online News Outlets | Variable, dependent on the outlet’s resources and standards. | Moderate, depending on the outlet’s verification procedures. |
| Social Media | Variable, reliant on user reporting and algorithmic detection. | High, due to the speed and ease of sharing. |
This table highlights the varying levels of verification and potential for misinformation across different news distribution channels. It’s crucial to critically evaluate the source and content regardless of the platform used. The potential for misinformation is always present, and careful consideration is necessary to avoid being misled.
Misinformation and Disinformation
Misinformation and disinformation are pervasive issues in the modern information landscape, significantly impacting public perception and trust in reliable sources. These phenomena, often intentionally misleading, can have serious consequences for individuals, communities, and society as a whole. Distinguishing between accurate and inaccurate information is increasingly challenging, necessitating critical thinking and a heightened awareness of potential manipulation.Understanding the methods used to spread these falsehoods and the challenges in countering them is crucial for navigating the complexities of contemporary information environments.
This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions and fosters a more resilient and discerning citizenry.
Definitions of Misinformation and Disinformation
Misinformation encompasses false or inaccurate information that is presented as factual. This can arise from unintentional errors, misinterpretations, or even deliberate attempts to mislead, but without the malicious intent of disinformation. Disinformation, on the other hand, is intentionally false or misleading information that is created, presented, and disseminated with the specific goal of deceiving or manipulating.
Methods of Spreading Misinformation and Disinformation
Various methods are employed to spread misinformation and disinformation, often leveraging the speed and reach of modern communication platforms.
- Social Media Platforms: Social media platforms, with their vast user bases and algorithms, can facilitate the rapid dissemination of false information. Targeted advertising and the use of bots or paid accounts can amplify the reach of misleading content.
- Fake News Websites: Websites designed to mimic legitimate news sources, often using sophisticated design and techniques, can disseminate misinformation and disinformation to a wide audience.
- Impersonation and Misrepresentation: The ability to impersonate individuals or organizations allows for the creation of false narratives or the manipulation of public discourse. This includes creating fake accounts, using stolen identities, and creating fraudulent profiles.
- Manipulated Media: The use of manipulated images, videos, and audio recordings can create entirely false scenarios or distort existing events to support false narratives.
Challenges of Identifying and Combating Misinformation
Identifying and combating misinformation presents significant challenges.
- Rapid Spread: The speed at which misinformation spreads online makes it difficult to contain or debunk false claims.
- Sophistication of Tactics: Misinformation campaigns are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it more difficult for individuals to distinguish between credible and fabricated information.
- Echo Chambers and Filter Bubbles: Online environments can create echo chambers where individuals are primarily exposed to information reinforcing their existing beliefs, making them less receptive to counterarguments.
- Lack of Resources: Combating misinformation requires substantial resources, including fact-checking teams and educational initiatives.
Examples of Misinformation Impacting Public Perception
Misinformation has a profound effect on public perception.
- Political Polarization: False narratives about political opponents or events can deepen societal divisions and political polarization.
- Public Health Crises: Misinformation about vaccines or public health measures can lead to distrust in scientific evidence and hinder public health initiatives.
- Economic Instability: Misinformation about economic policies or market conditions can create uncertainty and volatility in financial markets.
Role of Media Literacy in Combating Misinformation
Media literacy plays a crucial role in combating the spread of misinformation. It equips individuals with the critical thinking skills to evaluate information sources, identify biases, and assess the credibility of claims.
The Role of Transparency: Verified News Sources
Transparency in news reporting is paramount for maintaining public trust and credibility. It allows the public to understand the processes behind the news, enabling them to assess the reliability and objectivity of the information presented. A transparent news organization fosters a sense of accountability and builds public confidence in the media’s ability to report fairly and accurately.Transparency in news sources goes beyond simply disclosing the reporter’s name.
It encompasses a broader range of practices, including detailing the sources used, the methodology employed in gathering information, and any potential conflicts of interest. This detailed approach not only strengthens the credibility of the news organization but also promotes a more informed and engaged citizenry.
Importance of Source Attribution
Thorough source attribution is crucial for building trust. Readers need to understand the origin of the information presented. Vague or anonymous sources can undermine the credibility of a news report, making it difficult for the audience to assess the validity of the claims. Explicitly naming sources, when possible, allows for verification and further investigation. This is particularly vital when dealing with sensitive or controversial topics.
Transparency in Editorial Processes
News organizations should be open about their editorial policies and procedures. Clear guidelines on fact-checking, verification, and conflict of interest disclosure help build trust. This transparency allows the public to understand the mechanisms in place to ensure accuracy and objectivity in the reporting process. For instance, publishing the criteria used for selecting stories and the steps taken to verify information strengthens the organization’s commitment to journalistic integrity.
Examples of Transparent News Organizations
Many news organizations demonstrate a commitment to transparency. The Associated Press, renowned for its adherence to journalistic standards, consistently provides detailed information about their reporting methods and source verification processes. Similarly, the New York Times’ in-depth explanations of their fact-checking procedures and clear statements on editorial policies showcase their commitment to transparency. By meticulously detailing the processes behind their reporting, these organizations foster trust and credibility with their audiences.
Strategies for Building Trust and Credibility
Building trust and credibility is an ongoing process. News organizations can employ various strategies to enhance their transparency and accountability. One key strategy involves fostering open communication with the public through regular updates on editorial policies, clear statements on any potential conflicts of interest, and readily available contact information. Additionally, engaging in constructive dialogue with critics and actively addressing concerns demonstrates a commitment to accountability.
Implementing robust fact-checking procedures and clearly outlining the verification process is crucial. Furthermore, actively promoting diversity among journalists and editors can demonstrate a commitment to representing a broad range of perspectives.
Citizen Journalism and Verification
Citizen journalism, fueled by readily available technology, has dramatically reshaped news dissemination. Individuals, not just professional journalists, now capture and share information, often in real-time. This democratization of news gathering, while offering potential benefits, also presents unique challenges for verification and credibility assessment. Understanding the role of citizen journalists, their limitations, and the methods for evaluating their work is crucial for discerning credible information in today’s media landscape.Citizen journalism can be a valuable addition to traditional news sources, particularly in reporting on events happening locally or in areas with limited access to professional reporters.
It can also offer unique perspectives and insights not readily available through established channels. However, the lack of established editorial standards and verification processes inherent in citizen journalism can pose risks to accuracy and reliability. Evaluating the reliability of citizen journalists is essential to ensuring that the information shared is trustworthy and can be considered credible.
Role of Citizen Journalism in News Dissemination
Citizen journalism significantly amplifies the speed and reach of news dissemination. Social media platforms and online forums enable immediate sharing of events, often ahead of traditional news outlets. This immediacy can be invaluable, particularly during breaking news situations, offering eyewitness accounts and first-hand observations. However, this speed can also lead to the rapid spread of misinformation.
Challenges and Opportunities for Verifying Citizen Journalism
Verifying citizen journalism presents a complex set of challenges. Unlike professionally vetted sources, citizen journalists may lack the resources and expertise to thoroughly investigate and corroborate information. Determining the reliability of the source, including their location, experience, and potential bias, is often difficult. However, citizen journalism also offers opportunities. The diverse perspectives and experiences of citizen journalists can provide a wider range of narratives and insights, enriching news coverage.
Utilizing advanced tools and techniques, like image analysis and cross-referencing information across multiple sources, can enhance the verification process.
Evaluating the Reliability of Citizen Journalists
Assessing the credibility of citizen journalists requires a multifaceted approach. Factors to consider include the journalist’s experience, their potential bias, and the source of their information. A clear understanding of the context surrounding the event and the information provided is crucial. The use of multiple sources to verify claims and cross-referencing information across different platforms can significantly increase the reliability of citizen journalism reports.
Examples of Successful Citizen Journalism Projects and their Verification Methods
Numerous citizen journalism projects have demonstrated success in providing valuable information. For instance, citizen journalists played a key role in documenting natural disasters, providing timely updates on unfolding situations, and exposing instances of corruption. Verification methods in these instances often involved cross-referencing accounts, comparing images with official reports, and corroborating information through multiple independent sources.
Characteristics of Credible Citizen Journalism
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Information presented aligns with established facts and verifiable evidence. |
| Objectivity | The journalist presents information without personal bias or agenda. |
| Transparency | The source of the information and the journalist’s motivations are clearly stated. |
| Contextualization | Information is presented within its appropriate historical and social context. |
| Verification | Information is corroborated through multiple independent sources. |
Developing Media Literacy Skills
Cultivating media literacy is crucial in navigating the complex landscape of information dissemination. It equips individuals with the tools to critically evaluate news, discern fact from fiction, and form informed opinions. This involves understanding the processes behind information creation, distribution, and reception. Effective media literacy empowers individuals to be discerning consumers of information, ultimately contributing to a more informed and engaged citizenry.
Strategies for Developing Media Literacy Skills
Developing media literacy skills is a continuous process. Proactive engagement with diverse media outlets, coupled with critical analysis, is essential. Learning to identify bias, understand the motives behind information dissemination, and recognize common misinformation tactics are fundamental components of this process. Seeking out multiple perspectives and verifying information from reliable sources are also key strategies.
- Engage with a variety of media sources: Exposure to diverse perspectives across various platforms is vital. This includes news organizations, social media, blogs, podcasts, and documentaries. Actively seeking out diverse voices, rather than passively consuming information from only familiar sources, broadens understanding and helps identify potential biases.
- Learn to recognize and analyze bias: News organizations, like individuals, can exhibit biases. Understanding the potential for bias, and how it can influence reporting, is a crucial step. Consider the author’s background, potential conflicts of interest, and the overall tone of the article or content. This awareness enables a more nuanced interpretation of the information presented.
- Develop critical thinking skills: Critical thinking involves questioning information, rather than accepting it at face value. Evaluating the evidence presented, examining the source’s credibility, and considering alternative explanations are integral to this process. Analyzing the underlying assumptions and motivations behind the information is crucial.
Identifying and Avoiding Common Misinformation Tactics
Misinformation and disinformation tactics are often designed to manipulate and mislead. Recognizing these tactics is critical to avoiding their influence. This includes recognizing common patterns in the presentation of false information.
- Recognize emotional appeals: Emotional appeals, such as fear-mongering or outrage, are frequently used to sway opinions. Recognizing these appeals can help to discern if the information is based on genuine evidence or emotional manipulation.
- Identify false connections: Sometimes, misinformation creates false connections between unrelated events or ideas. Critically evaluate the logic and evidence presented to identify whether the information is truly connected or if the connection is fabricated.
- Be wary of sensationalized language: Sensationalized language and dramatic headlines can attract attention, but often lack substance. A critical eye helps to discern if the information presented is truly significant or merely designed to grab attention.
The Importance of Fact-Checking Skills
Fact-checking is a cornerstone of media literacy. It involves verifying information from reliable sources, such as reputable fact-checking websites or organizations. This skill is essential for distinguishing between accurate and inaccurate information.
- Consult reputable fact-checking websites: Reputable fact-checking organizations provide in-depth analysis and verification of information. Sites such as Snopes, PolitiFact, and FactCheck.org offer valuable resources to verify information.
- Verify information from multiple sources: Cross-referencing information from diverse, credible sources is crucial. This approach provides a more comprehensive understanding and reduces the risk of misinterpretation.
- Seek out diverse perspectives: Considering various perspectives on an issue can enhance understanding and help to identify potential biases. Consulting experts in the field, or researching multiple accounts, allows for a richer understanding.
Verifying Information from Multiple Sources
Verifying information from multiple sources enhances the accuracy and reliability of the information. Consulting various perspectives can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Compare information from different news outlets: Comparing information presented by different news organizations allows for a broader perspective and can reveal potential biases or inaccuracies in a single source.
- Evaluate the credibility of each source: Considering the reputation, history, and methodology of each source is essential. Reliable sources typically adhere to journalistic standards and ethical principles.
- Consider the overall context: Evaluating the overall context of the information helps in understanding the potential motivations and biases behind the information presented.
Tools for Verification
Verifying news sources requires a multifaceted approach. Beyond simply examining a publication’s reputation, effective verification leverages various tools and techniques. This section explores the critical role of fact-checking resources, search engine strategies, and digital tools in discerning credible information.Fact-checking organizations play a crucial role in verifying the accuracy of news claims. These organizations employ rigorous methodologies to assess the validity of information presented in news articles and statements.
Staying informed about current events is crucial, and relying on verified news sources is paramount. Checking out reputable sources like world news headlines is a great way to get a good overview of global happenings. Ultimately, vetting sources is key to understanding the world’s events accurately.
Their work helps individuals distinguish between accurate reporting and potentially misleading content.
Fact-Checking Websites and Resources
Fact-checking websites and resources are invaluable tools for verifying information. These independent organizations meticulously examine claims and statements, providing detailed analysis and evidence to support their findings. Their goal is to identify inaccuracies and promote accurate reporting.
Staying informed is key, and for that, you need reliable sources. Checking a reputable daily news update, like daily news update , can be a good starting point. However, always double-check the source’s verification process to ensure the information is accurate before you form your own opinion.
- Snopes: A well-known fact-checking website that investigates a wide range of claims, from urban legends to political statements. It utilizes a variety of sources and methods to assess the veracity of information.
- PolitiFact: This resource focuses specifically on political claims, providing in-depth analyses of statements made by political figures. It utilizes a scoring system to rate the accuracy of claims, enabling users to understand the reliability of the information.
- FactCheck.org: This nonpartisan organization assesses claims made by candidates and other political figures. Its work provides a valuable resource for evaluating the accuracy of political statements.
Utilizing Search Engines for Verification
Search engines are powerful tools that can be employed for verifying information. By strategically utilizing search operators and filters, users can gain a deeper understanding of the context and origins of a news item.
- Advanced Search Operators: Employing advanced search operators like “site:” and “filetype:” allows users to narrow their search results, focusing on specific websites or file types (e.g., academic papers, government reports). This precision helps in verifying the source of the information.
- Evaluating Search Results: Critically evaluate the search results. Look for multiple sources corroborating the same information, or for significant discrepancies. The quantity and diversity of supporting sources are important indicators of reliability.
- Checking for Citations: Note the citations provided in news articles or online sources. Following up on those citations helps determine the origin of the information and adds a layer of verification.
Employing Digital Tools for Verification
Digital tools offer a range of possibilities for verifying news. These tools often combine elements of fact-checking and investigative journalism.
- Source verification tools: These tools can help assess the credibility of a news source by examining its history, authorship, and publication practices. Tools like these can help determine if the news source is credible and reputable.
- Reverse image search: Utilizing reverse image search through Google Images or other platforms allows users to identify the origin of images and verify if they’re being used accurately or if they have been manipulated. This process helps identify potentially fabricated content.
- News aggregators and fact-checking extensions: Many news aggregators and web browsers have integrated fact-checking extensions. These extensions provide immediate checks for the veracity of articles or social media posts. These extensions often link to reliable fact-checking websites, making the verification process seamless.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, navigating the complexities of the modern news landscape requires a proactive approach to media literacy. By understanding the processes behind verified news sources, including verification methods, credibility assessment, and the identification of bias, individuals can become more discerning consumers of information. This knowledge fosters informed decision-making and promotes a healthier understanding of the world around us.
Top FAQs
What are the key characteristics of a verified news source?
Reputable news organizations typically exhibit transparency in their reporting, employ diverse perspectives, and utilize rigorous verification processes to ensure accuracy.
How can I identify potential bias in a news source?
Look for patterns in the language used, the sources cited, and the overall presentation of information. A lack of balanced perspectives, an overemphasis on specific viewpoints, or the promotion of certain agendas can signal bias.
What role do fact-checking organizations play in verifying news?
Independent fact-checking organizations play a critical role in scrutinizing news claims, providing an objective assessment of accuracy, and helping to identify misinformation.
How can I evaluate the credibility of a citizen journalist?
Consider the source’s experience, reputation, and verification methods. Look for evidence of their expertise and commitment to accuracy, and whether they’re using reliable sources.






